Since last summer, StalkPhish.io, our advanced platform dedicated to combating bank fraud, phishing, and scams, has been upgraded with a system for classifying phishing kits. This enhancement allows us to effectively categorize phishing kits collected through our infrastructure, bringing a new level of insight and prevention for businesses facing phishing threats. PhishingKit-Yara-Rules: An Open Source
Category: PhishingKit-Yara-Rules
This phishing kit impersonates Caisse D’Epargne, a French bank, of BPCE Group. This kit was downloaded at the beginning of December 2023, by our phishing detection and investigation tool StalkPhish.io. About the phishing kit The configuration files contained in the downloaded ZIP archive were edited between November 30 and December 1, 2023: This phishing kit
Find a short analysis of the “Greatness” phishing kit used by a new Phishing as a Service infrastructure. Added some original IOCs for detection and hunting.
An analysis of a Coinbase phishing kit designed to steal personal data, login, password and the second factor of authentication (MFA/2FA).
Fight phishing (aka “Phight”) is not an easy task, you need to detect a campaign before starting to dismantle it. You can compare that to a race: the faster you detect a campaign, the faster you can start to takedown it! We created StalkPhish with this idea in mind, to be fast and accurate. Fast
At StalkPhish we like dissecting Phishing kits, first because we create Yara rules for detection, secondly because we must continually keep up to date with new developments in terms of phishing kits, finally because we like to pass on to the general public knowledge about this type of threat. This post was previously published on
One of the latest kits downloaded by StalkPhish targets customers of the online bank M&T. It has a special feature that we wanted to share with you. We still blogged about the use of Telegram by scammers, but this kit present an interesting new trick. First observations As many, the archive of this kit has
At StalkPhish we like dissecting Phishing kits, first because we create Yara rules for detection, secondly because we must continually keep up to date with new developments in terms of phishing kits, finally because we like to pass on to the general public knowledge about this type of threat. The phishing kit we go to
As a reminder, the PhishingKit-Yara-Rules project is a free and open source project which provides several dozen phishing kit detection rules contained in zip archives. You can find these rules on GitHub: https://github.com/t4d/PhishingKit-Yara-Rules We have already covered the creation and use of Phishing Kit Yara rules in a previous post (see: https://stalkphish.com/2021/08/17/using-phishing-kit-yara-rules-project-for-phishing-kits-detection-and-triage/). Specifically, these are
Since some months now, we maintain specific Yara rules to detect phishing kit sources (.zip files). Phishing kits sources are sometimes left on the host serving phishing pages. Using the StalkPhish project (see https://stalkphish.com/products/stalkphish/) we used to collect phishing kits in order to extract e-mails addresses, Telegram channels (see https://stalkphish.com/2020/12/14/how-phishing-kits-use-telegram/), and so on. In order
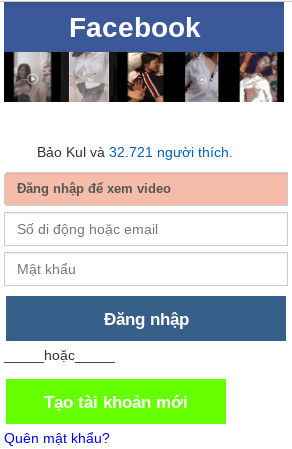
Analysis of a Facebook phishing kit which exfiltrate stolen data to an online Google Sheet using ajax POST method.